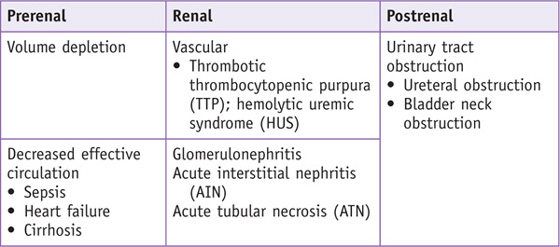
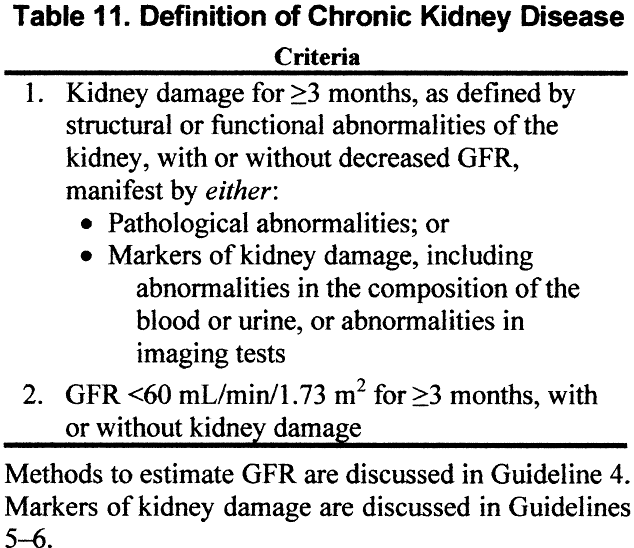
Learn about the icd-10 coding for bilateral nephrolithiasis, including when to use n20. 2 and n13. 2, documentation requirements, and common coding pitfalls. Accurate and thorough documentation is essential for appropriate coding and reimbursement when treating kidney stones. Yes, but using n20. 2 is more specific and often preferred when both renal and ureteral stones are present … Individuals with a history of recurrent kidney stones may be at increased risk for developing chronic kidney disease or experiencing complications such as obstructive uropathy. Nephrolithiasis, also known as kidney stones or renal calculi, refers to the presence of stones within the kidneys. · in this article, we will explore the medical coding and billing guidelines for kidney stones, including common codes, diagnostic codes, procedural codes, and billing best practices. · read this comprehensive guide to kidney stone icd-10-cm codes, which includes necessary codes, clinical information, billability, synonyms, and faqs. Explore icd-10 coding for renal stones, including kidney and ureteral stones. Knowing the difference between primary and secondary … · examples of common stone locations and their corresponding icd-10-cm codes include: Only use n20. 0 when your provider documents kidney stones. It is one of the most common kidney diseases in adults. Learn about documentation requirements and common coding pitfalls. · coding for kidney stones, or ureterolithiasis and nephrolithiasis, requires a deep understanding of icd-10 guidelines. Can i code both n20. 1 and n20. 0 if stones are found in both locations? The following clinical details must be clearly documented to support …
Shocking Icd 10 Code For Bilateral Kidney Stones Are You At Risk
Learn about the icd-10 coding for bilateral nephrolithiasis, including when to use n20. 2 and n13. 2, documentation requirements, and common coding pitfalls. Accurate and...